|
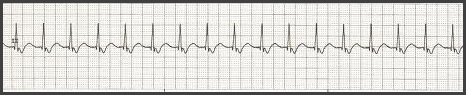
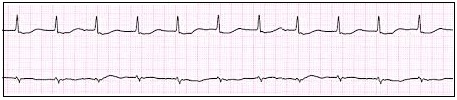
If a Junctional rhythm has a heart rate above 100 bpm, it is called “Junctional Tachycardia”. Many times it starts out as accelerated junctional (60 to 100 bpm), but often the heart rate increases above 100 bpm and becomes Junctional Tachycardia. There may be AV dissociation or retrograde P waves (P waves that follow the QRS). In the example above, it shows a junctional tachycardia rhythm having inverted P waves following the QRS (retrograde). This is example is described as “junctional escape”. Below is an example of an Accelerated Junctional Rhythm. In this example, the P waves are absent which also makes it an escape rhythm. Ischemia and digitalis intoxication are the two most common causes for junctional rhythms. |
Return to Home Page
