
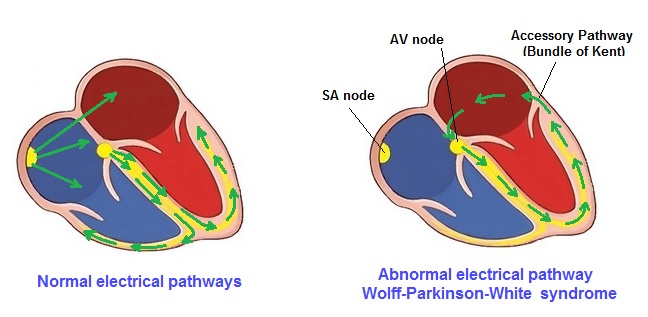
 WPW’s abnormal pathway does not share the rate-slowing properties such as with the AV node. Normally the AV node serves as a "gatekeeper", limiting the rate of electrical signals that it allows to get through to the ventricles. In situations where the atria generate excessively rapid electrical activity (such as A-fib or A-flutter), the AV node will limit the number of signals conducted to the ventricles. However with WPW, this accessory pathway may conduct electrical activity at a significantly higher rate. For instance, in the example above, if the atrial rate was 300 beats per minute, the accessory pathway may directly conduct all the electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles, causing the to contract at 300 beats per minute. Extremely rapid heart rates such as this may result in hemodynamic instability cardiogenic shock. In some cases, the combination of an accessory pathway and cardiac dysrhythmias can trigger V-Tach or V-Fib, a leading cause of sudden cardiac death. Symptoms Some people with WPW have only a few episodes of rapid heart rate while others may have a rapid heart rate once or twice a week, or more. Usually with WPW, the patient will have symptoms depending on the heart rate, and sometimes there may be no symptoms at all. This condition is determined or discovered upon 12 lead test results. Symptoms from WPW include: Exams, Tests and Treatment; A physical exam done during a tachycardia episode will show a heart rate faster than 100 beats per minute. A normal heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute in adults, and under 150 beats per minute in newborns, infants, and small children. Blood pressure will be normal or low in most cases. The long-term treatment for WPW syndrome usually involves needing a catheter ablation.. The type of ablation that is performed, enters into the area of the abnormal pathway, and is closed using a special type of energy called radiofrequency or by freezing it (cryoablation). Open heart surgery can provide means to burn or freeze the extra pathway shut, thus providing a permanent cure for WPW. In most cases, this procedure is done only if there are other reasons for needing open heart surgery. Is Wolf White Parkinson syndrome hereditary? Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is one of a classification of pre-excitation disorders that have been found to have a genetic component. Recent research has identified the gene (PRKAG2) with WPW associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and conduction system disease. Outlook (Prognosis) Catheter ablation cures this disorder in most people. The success rate for the procedure ranges between 85% to 95%. Success rates will vary depending on the location and number of extra pathways. |
Return to Home Page
